- In the piecemeal distribution of cash during the dissolution of a partnership firm, the balance sheet shows:
Capital a/c for Mr. X : Rs. 2,000
Capital a/c of Mr. Y : Rs. 3,000
Creditors : Rs. 5,000
Mr. X’s Loan : Rs. 5,000
If the available cash balance is Rs. 8,000 who should be paid?
(a) Creditors Rs. 5000, Mr.X’s Loan Rs. 3000
(b) Creditors Rs. 4000, Mr.X’s Loan Rs. 4000
(c) Mr.X’s Loan Rs. 5000, Creditors Rs. 3000,
(d) All parties are equally distributed Rs. 2000. - Which of the following is NOT true regarding Depreciation Accounting?
(a) Depreciation is an amortised expenditure.
(b) Depreciation cannot be provided in case of loss in a financial year.
(c) Depreciation is process of allocation of cost of fixed assets over the lifetime of that assets.
(d) Reducing balabce method of depreciation is followed to have a uniform charge for depreciation and repairs and maintenance together. - The main objective of preparing price level change accounting if to
(a) Match the financial report to the current price levels.
(b) Inflate the values based on a predetermined factor price.
(c) Provide a favourable financial statement revealing better profits and financial position.
(d) All of the above. - Ownership of the goods under installment payment system is transferred at payment system is transferred at the time of
(a) Payment of first installment
(b) Payment of last installment
(c) Receiving delivery of goods
(d) Immediately after the purchase agreement - The correct formula for calculating profit under incomplete records
(a) Net profit = Opening capital + Additional capital during the year + drawing
(b) Net profit = closing capital + Drawing + Opening capital
(c) Net profit = Closing capial – Drawing + Additional capital during the year – Opening capital
(d) Net profit = Closing capial + Drawing – Additional capital during the year – Opening capital - which of the following item is not shown in the receipt and payment account of an organisation?
(a) Payment of previous year outstanding salary
(b) Current year outstanding salary
(c) Receipt of advance subscription for next year
(d) Prepaid rent for next year - Profit or loss on voyage account is transferred to
(a) Profit and loss account of shipping company
(b) Balance sheet
(c) Trial balance
(d) None of these - Which of the following company/companies are registered by the companies Act 2013?
(a) Banking Company
(b) Government Company
(c) Private Company
(d) All of the above - What is the limit to the number of members in a private company?
(a) 50
(b) 200
(c) 20
(d) 7 - The whole process of the company formation can be divided into three direct stages,the sequence is-
(a) Promotion, incorporation by registration, commencement of business
(b) Promotion,commencement of business,incorporation by registration
(c) incorporation by registration,commencement of business,Promotion
(d) commencement of business,incorporation by registration,Promotion - As per the Sec. 2(71). of Companies Act, 2013, a private limited company, which is a subsidiary of a public company, shall be deemed as-
(a) Public company
(b) Private company
(c) Government company
(d) Semi private company - Match the following
A. Authorised capital a. Reserves their preference in dividend
B. Preference share b. Called up only on liquidation of company
C. Reserve capital c. Unit of a fixed small amount in share capital
D. Share d. Maximum amount of share capitalA. B. C. D.
a. iv, iii, ii, i
b. iv, i , ii ,iii
c. iii, i ,iv, ii
d. iv, ii, i, iii - If a share of Rs. 10 on which Rs. 7 has been called and Rs. 3 is paid, has forfeited, the share capital account should be debited with
(a) Rs. 3
(b) Rs. 4
(c) Rs. 7
(d) Rs. 10 - 50000 equity share of Rs. 10 each were issued to public at a premium of Rs. 2 per share payable on allotment. Applications were received for 60000 shares. amount of securities premium account will be-
(a) Rs.1,00,000
(b) Rs.1,20,000
(c) Rs.20,000
(d) Rs.10,000 - If the loss on reissue of share is than the amount forfeited, the surplus amount is transferred to
(a) Share capital a/c
(b) Capital reserve a/c
(c) General reserve a/c
(d) Profit & loss a/c - Rights share are issued to-
(a) Promoters for their service
(b) Holders of convertible debenture
(c) Existing shareholders
(d) all of the above - Which of the following statement is NOT true regarding buy back of shares?
(a) Buy back must be authorised by articles of association.
(b) A special resolution must be passed for buy back.
(c) Maximum buy back limit in any year is 25% of total paid up equity capital and free reserve.
(d) Shares can be partly paid up. - Which of the following reserve is not available for issue of fully paid bonus share?
(a) Profit and loss account
(b) Capital redemption reserve
(c) Capital reserve arising due to revaluation of fixed assets
(d) Security Premium - If the share of smaller denomination are converted into the shares of higher denomination without changing the total amount of share capital it is a case of
(a) Consolidation of share capital
(b) Split of share capital
(c) Sub-division of share capital
(d) Decrease in unissued share capital - Which of the following is not the source for redemption of preference share?
(a) Credit balance of P/L a/c
(b) General Reserve
(c) The proceeds of a fresh issue of shares
(d) the proceeds of issue of debentures - A Ltd. acquired a machine of Rs. 6,60,000 from B Ltd. A Ltd. discharged the consideration by issuing 12% debentures of Rs. 100 each at a premium of 10%. The number of debentures received by B limited wil be-
(a) 5,400
(b) 54,000
(c) 60,000
(d) None of these - Intrest on debentures issued as a collateral security is paid on_
(a) Face value of debenture
(b) Issued price of debenture
(c) No interest is paid
(d) Paid up value of debenture - If debenture purchase in open market are not immediately cancelled,they are treated as-
(a) Investsment
(b) Current asset
(c) Current liabilites
(d) Capital - According to the companies Act 2013, Profit and loss statement of a company is required to be prepared in the format given in
(a) Schedule III part-I
(b) Schedule III part-II
(c) Schedule III part-III
(d) Table A - Match under what heading would following items in List-A appear in the balance sheet of a company given in List-B
List-A List-B A. Goodwill i. Other current liabilities B. Unpaid Dividends II. Other current asset C. Prepaid Expenses III. Intangible asset D. Call- in- Arrears IV. Shareholders’ fund (a) III,I,IV,II
(b) III,IV,I,II
(c) III,I,II,IV
(d) IV,III,I,II - What would be the maximum remuneration rate on net profit computed as per section 198, if there is only one whole time director?
(a) 3%
(b) 5%
(c) 10%
(d) 11% - A company wishes to pay dividend on shares. state which of the following may be used for this purpose-
(A) Premium on shares
(B) General reserve
(C) Profit on sale of land
(D) Free reserve(a) All of the above
(b) Only B,C,D
(c) Only B and D
(d) Only B - The bill purchased/discounted become NPA if the bill remains overdue for a period of more than
(a) 90 days
(b) 60 days
(c) 30 days
(d) 1 year - Which of the following is the regulator of insurance sector on India?
(a) RBI
(b) ICAI
(c) IRDA
(d) SEBI - Actual profits of a firm is Rs.35,000. the rate of normal returns is 10% p.a. the average capital employed is Rs. 25,0000 what is the amount of goodwill as per capitalised method of profit?
(a) Rs. 35,0000
(b) Rs. 2,000
(c) Rs. 2,15,000
(d) Rs. 1,00,000 - Given:
Paid up value of an equity share 50%
Normal rate of return 8%
Expected future dividend rate 4%
What is the value of an equity share under the yield method?
(a) Rs. 50%
(b) Rs. 100%
(c) Rs. 25%
(d) Rs. None of above - Which of the following statement is false regarding internal reconstruction of company?
(a) Under internal reconstruction, the existing company remains as it is only capital structure is changed.
(b) After internal reconstruction ,company may come out of the loss position and enter the position of earning profits.
(c) Accounting standard-14 is applicable for internal reconstruction of company.
(d) A company must pass a special resolution for reduction of capital under internal reconstruction. - At the time of amalgamation, purchase consideration does not include-
(a) the sum which the transferee company directly paid to the creditors of the transferor company.
(b) Payment made in form of asset by the transferee company to the shareholders of the transferor company.
(c) Payment made by transferee company on the basis of ratio of intrinsic value of share of transferee and transferor company.
(d) Preference share issued by the transferee company to the preference shareholders of the company. - The share of outsiders in the net assets in subsidiary company is known as under-
(a) Outsider’s Liability
(b) Minority Intersted
(c) Otusider’s Assets
(d) Majority interest - H Ltd. holding company sold goods worth Rs. 40,000 to S Ltd. subsidiary company at a profit of 25% on cost price. If goods worth Rs. 1,000 is remaining in the stocck of S ltd What is the amount of analysed profit for the purpose of preparing consolidated B/S ?
(a) Rs.2,0000
(b)Rs. 2,500
(c)Rs.2,500
(d) Rs.1,500 - When a company is wound -up all person who ceased to be the shareholders within a year before the winding up are placed in the-
(a) ‘A’ list of contributors
(b) ‘B’ list of contributors
(c) ‘C’ list of contributors
(d) ‘D’ list of contributors - At the time of liquidation a company has following liabilities
A. Creditors Rs. 5000
B. Legal expenses Rs. 1500
C. Liquidation expenses Rs. 290
D. Preference share capital Rs. 7200
What will be the order of payment while preparing the liquidator final statement of account?
(a) B,A,D,C
(b) C,B,A,D
(c) C,B,D,A
(d) B,C,A,D - Under the double account system, match the following items to their respective accounts:
A. Equity share capital i. Revenue Account
B. Interest on debenture ii. General balance sheet
C. Management expenses iii. Receipt and expenditure on capital
D. Sundry creditors iv. Net revenue account
(a) iii,iv,i,ii
(b) ii,iv,i,iii
(c) ii,i,iv,iii
(d) iv,i,iii,ii - Under the arrangements of Government accounting which of the following fund is not maintained by the government of India?
(a) consolidated funds
(b) Research and development fund
(c) Contingency fund
(d) Public account - A family engaged in agriculture work consumed food grain of Rs. 5000 for his family.
‘Its journal entry would be under Accounting for a agriculture farms’
(a) Crops a/c Dr. 5,000
To cash a/c 5,000
(b) Wages a/c Dr. 5,000
To crops a/c 5,000
(c) Drawings a/c Dr. 5,000
To crops a/c 5,000
(d) No entry - Forensic accounting is a combination of-
(a) Accounting auditing & Investigation
(b) Accounting and Auditing
(c) Only Accounting
(d) None of these - Social accounting can be defined as
(a) an independent discipline to measure and report the activities of an entity which affects the society.
(b) the application of accounting in the field of social sciences.
(c) process of ordering,measuring and disclosing the impact of exchanges between a firm and its social environment.
(d) All of the above. - MFIs provide vital financial services to the economically deprived members of the society.
Here MFIs stand for
(a) Mutual fund Institutes
(b) Micro-finance Institutes
(c) Money and financial Institutions.
(d) Monetary financial service of India. - Fixed cost per unit__________ with increase in the size of output.
(a) decreases
(b) increases
(c) remain same
(d) can’t say - Match the following column-A to colum-B
Colum- A Colum – B A. Interior designing i. Multiple B. Automobile ii. Batch C. Sugar iii. Process D. Toys iv. Job (a) ii,iv,iii,i
(b) ii,iii,iv,i
(c) iv,i,iii,ii
(d) iv,ii,iii,i - Which of the expenses given below is not included in factory overheads?
(a) Store keeping expenses
(b) Drawing office expenses
(c) Carriage outward
(d) Haulage expenses - A cost incurred in the past that cannot be changed by any future action is called-
(a) Relevant cost
(b) Shutdown cost
(c) Out of pocket cost
(d) Sunk cost - Following information are available for the ABC Hotel for the month of April.
No. of rooms available per night – 50
Percentage occupancy achieved – 70%
Room servicing cost – Rs. 10,125
The room servicing cost per occupied room night for the given period would be to the nearest rupees
(a) Rs. 5.45
(b) Rs. 9.00
(c) Rs. 49.82
(d) Rs. 112.50 - The cost incurred upto the point where individual products can be identified is called
(a) Prime cost
(b) Average cost
(c) Separation cost
(d) Joint cost - State which the following is/are correct for uniform costing method-
(A) It is also known as composite costing
(B) This method of costing is used where units produced in a batch are uniform in nature and design.
(C) It is a system in which a number of firms in the same industry use the same method of costing.
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) Only C
(d) Only A and B - In contract costing method direct labour cost is debited to
(a) Contract a/c
(b) Work in Progress a/c
(c) Contractee a/c
(d) None of these - In a process X 10,000 units were put into process at cost of Rs. 2,00,000. The amount of wage and overheads was Rs.3,00,000 and Rs. 1,70,000 respectively.
normal wastage was 5% wastage is sold @ Rs. 10 per unit. the actual production is 9400 units. the value of abnormal wastage is-
(a) Rs. 77 per unit
(b) Rs. 78 per unit
(c) Rs. 72 per unit
(d) Rs. 70 per unit - Inter process profit arises, when output of one process is transferred from one process to another at which price?
(a) Market price
(b) Cost price
(c) Actual price
(d) Realised price - Secondary packing expenses are the part of-
(a) Prime cost
(b) Production overhead
(c) Administrative cost
(d) Distribution cost - Which of the following activities may be involved in administrative expenses?
(a) Salary of Board of Directors and Secretarial staff.
(b) Allowance of public relation officer.
(c) Fees of statutory auditors
(d) All of the above - Which is the following statement is not true for non integra system?
(a) Separate ledgers are maintained for cost and financial accounts.
(b) it is based on double entry system
(c) cost accounts are concerned with personal accounts.
(d) under this system one main ledger i.e. cost ledger and various subsidiary ledger are maintained. - In which accounting system whereby cost and financial accounts are kept in the same set of books?
(a) Integrated accounting system
(b) Non integrated accounting system
(c) Cost control accounts
(d) None of the above - Stores ledger control a/c Dr. to cash a/c State, under integrated accounting system, what is the above journal entry is showing-
(a) Material purchased for stock on cash
(b) Material purchased for stock on cash
(c) Material purchased for specific job
(d) Payment to creditors - Which of the following is incorrect equation of contribution?
(a) Sales – Variable cost
(b) Fixed cost + profit
(c) Sales – Fixed cost
(d) Sales – Marginal cost - A company produced 700 units of a product and incurred the following cost:
Direct material Rs. 15,000
Direct wage Rs. 20,000
Overheads(20% fixed) Rs. 50,000
If the sale value of 700 units was Rs. 1,20,000, what is the contribution margin?
(a) 74%
(b) 75%
(c) 35.5%
(d) 37.5% - Which of the following is not a relevant coast information in a make or buy decision?
(a) Cost to buy
(b) General fixer cost
(c) Incremental cost
(d) Opportunity cost - In a shutdown decision one has to consider-
(a) Contribution
(b) Identifiable fixed cost, if any
(c) Impact of shutdown on other products if any
(d) Both 2 and 3 - Marginal costing is also known as
(a) Indirect costing
(b) Direct costing
(c) Variable costing
(d) Both 2 and 3 - Which of the following statements correctly shows the BEP analysis?
A. No profit, No loss
B. Total revenue = Total cost
C. Contribution = fixed cost
(a) Only A
(b) Only A,B
(c) All A,B,C
(d) Only C - The margin of safety for a firm in a very volatile market is 5%. which of the following is true?
(a) The margin of safety is probably too high.
(b) The margin of safety is probably too low.
(c) The margin of safety is adequate.
(d) None of the above - Which is the following is financial budget?
(a) Capital expenditure budget
(b) Working capital budget
(c) Cash budget
(d) All of above - Production budget is dependent on
(a) Material budget
(b) Cash budget
(c) Sales budget
(d) Research and development budget - Match the following:
A. ZBB i Summary of all functional budget B. Master budget ii. Changes according of production level C. Budgeting iii. No previous level expenditure D. Flexible budget iv. Process of preparing budget (a) iii,i,iv,ii
(b) iii,i,iv,ii
(c) iv,ii,i,iii
(d) iv,iii,ii,i - Standard costing is a technique of
(a) Anticipating cost
(b) Cost control
(c) Reducing losses of business
(d) Calculating standard cost for the product - Material cost variance is equal to
(a) MPV + MUV
(b) MPV + MYV
(c) MMV + MYV
(d) MPV + MMV - The difference between actual cost and standard cost is known as
(a) Expenditure
(b) Income
(c) Variance
(d) Standard cost - Which statement is true regarding labour idle time variance?
(a) Abnormal idle is always hourly rate
(b) This variance is always unfavourable or adverse.
(c) This variance represents the segment of labour rate variance.
(d) This variance is not caused by non-availability of raw material. - When actual sale price is higher or lower than the standard price, it is called?
(a) Sales quantity variance
(b) Sales revenue variance
(c) Sales price variance
(d) Sales mix variance - Calculate fixed overheads cost variance:
Standards Actual
fixed overheads Rs.8,000 Rs. 8,500
out put in units 4000 3800
(a) 900(A)
(b) 500(A)
(c) 900(F)
(d) 500(F) - Under activity based costing system which type of costs are assigned to activities using resources drivers?
(a) Direct costs
(b) Indirect costs
(c) Total cost
(d) None of these - A transfer price is
(a) the price to turn profit centres into investment centres.
(b) a market based pricing to sell a product.
(c) the price changed by one segment of the company to another segment.
(d) All of the above. - Life cycle cost of a product includes-
(a) Pre Acquisition
(b) Maintenance costs
(c) End of life profit price
(d) Negotiated transfer price - When a ready market exists,the best transfer price will probably be the
(a) Market price
(b) Variable price
(c) Full cost plus profit price
(d) Negotiated transfer price - The real time feature in EDP, normally would be least useful when applied to accounting for a firm’s
(a) Bank account balances
(b) Customer accounts receivable
(c) Merchandise inventory
(d) Property and depreciation - What are the advantages of using computers for cost control and cost reduction?
(a) Time saving
(b) Keeping track of information
(c) Increase mobility ans efficiency
(d) All of the above - Productivity =
(a) Profit/Output
(b) Cost/Output
(c) Output/Input
(d) Input/Output - From the following data, calculate productivity for the product X:
Standard
time per unit 5 Hrs/Metre
Production 4000 metre
time taken 25,000 Man Hours
(a) 1.25
(b) 0.80
(c) 6.25
(d) 0.88 - Which of the following is not the objective of management accounting?
(a) Efforts to achieve goals of planning
(b) Calculation of per unit cost of a product
(c) Screening of inferred opportunities and hurdles
(d) Development of alternative and determination of best alternative - Management accounting is an extended technique-
(a) Financial accounting
(b) Decision accounting
(c) Tax accounting
(d) Cost accounting - Current ratio is-
(a) Equals to quick ratio
(b) Equals to absolute quick ratio
(c) Less than liquidity ratio
(d) More than Liquidity ratio - Difference in capital gearing ratio and debt equity ratio is due to
(a) Preference share is due to
(b) Equity share capital
(c) Both a and b
(d) Neither a nor b - A ltd. has an average stock is Rs. 50,000 and stock turnover ratio is 8 times. it sales goods at a profit of 25% on cost. its gross profit ratio will be-
(a) 25%
(b) 16.67%
(c) 20%
(d) 50% - There is a flow in funds when
(a) there is a transaction between a non current account item and current account item.
(b) there is a transaction between a non current asset item and non current liability.
(c) there is a transaction between a non current liability and current asset.
(d) All of the above. - Received dividend on investment Rs. 18,000 out of which Rs.2,800 is out of preacquisition profits.
(a) Rs.2,800
(b) Rs.18,000
(c) Rs.20,800
(d) Rs.15,200 - Which is the following are applications of fund?
(A) Decrease in share capital
(B) purchase of fixed assets
(C) decrease in long term liabilities
(D) payment of tax(a) payment of tax
(b) A and C only
(c) A and D only
(d) None of these - Cash equivalents mean
(a) Cash balance
(b) Bank balance
(c) Trade investment
(d) Short term investments in liquid securities - Issue of equity shares for consideration of purchase of land is-
(a) neither a source nor an application of cash and cash equivalents.
(b) an application of cash and cash equivalents.
(c) a source of cash and cash equivalents.
(d) None of these. - Which is following is statement is not correct regarding cash flow ananlysis:
(a) Cash flow are inflow and outflows of cash and cash equivalents
(b) Decrease in creditors, decreases cash.
(c) Cash flow statement is mandatory for all business firm.
(d) Working capital from business operations can be determined from income statement. - Match the following financial information to its related activity:
A. Buy back of equity share i. No cash flow
B. Interest received on long term investment ii. Operating activity
C. Cash payment to supplier iii. Investing activity
D. Cash deposited into bank iv. Financial acticity(a) iv,iii,ii,i
(b) iv,ii,iii,i
(c) iii,i,ii,iv
(d) i,iii,ii,iv - The term ‘Capital structure’ refers to-
(a) Current assets – current liabilities
(b) Equity share capital + reserve and surplus
(c) Long term debt + Outside creditors
(d) Long term debt + Preferred stock and common stock equity - The traditional approach towards the valuation of a company assumes-
(a) that markets are perfect.
(b) that there is an optimum capital structure
(c) that total risk is not altered by changes in the capital structure
(d) that the overall capiatalization rate holds constant with changes in financial leverage. - The pecking order theory of capital structure is based on
(a) Asymmetric information
(b) Symmetric information
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above - In a firm cost of equity the systematic risk of an ordinary share in relation to the market is called as
(a) Expected risk
(b) Industry risk
(c) Beta risk
(d) Returning risk - Investors personal tax rate is taken into consideration while computing cost of
(a) equity capital
(b) debt capital
(c) preference share capital
(d) retained earning - Cost of capital does not mean
(a) Cut off rate decided by management
(b) maximum anticipated rate of return
(c) opportunity cost
(d) expectation of investors for dividend - The circular flow concept of working capital is based upon
(a) operating cycle of a firm
(b) current assets cycle
(c) traditional cycle
(d) production cycle - In heading or matching approach permanent working capital is financed by
(a) current liabilities
(b) current assets
(c) sources of long term finance
(d) sources of short term finance - The relationship between sales and working capital is given by the equation:
(a) x = ay + b
(b) y = a + bx
(c) y = ba + x
(d) x = a + bx - Which of the following is not true regarding capital budgeting decisions?
(a) NPV is the method of evaluating long term investment proposals.
(b) In the case of independent investment proposals IRR and NPV method provides the same results.
(c)Two mutually exclusive projects have been evaluated.project A has NPV of Rs. 8 lack and IRR of 16%; project B has 18%. since project B has higher IRR, it should be selected.
(d) Payable method determines the number of years required to recover initial investment outlay. - Which of the following method ignores the time value of money?
(a) Accounting rate of return method
(b) Profitability index method
(c) Internal rate of return
(d) Net present value method - A view that the divided policy of a firm has a bearing on share valuation advocate by James Walter is based on which one of the following assumption?
(a) Cost of capital does not remain constant.
(b) retained earning is only source of financing.
(c) Earning per share fluctuates.
(d) All of the above. - Match the following:
A. Traditional model i. stock market places more weight on dividends than on retain earning B. Dividend discount model ii. dividends Irrelevance C. Gordon method iii. Dividends are discount by the cost of equity share capitial D. MM Model iv. Dividends capitalization approach (a) iii,i,ii,iv
(b) iv,iii,i,ii
(c) i,iii,iv,ii
(d) ii,iii,i,iv - Which is the following is not true for the balanced scorecard?
(a) Top down reflection of mission and streategy
(b) Based on traditional financial measures
(c) Integrates external measures
(d) Helps to focus on company strategic agend - The balance scorecard looks at organisational performance from four perspectives. which one of the following is not included?
(a) The learning and growth perspective
(b) The customer perspective
(c) the social perspective
(d) the financial perspective - Which of the following statements are correct?
Statement-I: ROI is calculated as the ratio of investment center income to invested capital.
Statement-II: EVA measures earning after the cost of capital
Statement-III: MVA is the shareholder’s appraisal of the firms efficiency.
(a) Statement-I,II
(b) Statement-I,III
(c) Statement-I,II,III
(d) Statement-II,III - Which of the following is/are the statistical technique for risk analysis?
(a) Probability
(b) Variance or standard deviation
(c) Coefficient of variation
(d) All of the above - According to the responsibility accounting the entire organisation is divided into various-
(a) Value streams
(b) Activities
(c) Responsibility centres
(d) Target centres - The reason of operating leverage is-
(a) Fixed Operation costs
(b) fixed financial costs
(c) Higher rate of tax on taxable income
(d) All of the above - Combined leverage is equal to
(a) Operating leverage into financing
(b) Operating leverage + financing leverage
(c) Operating leverage – financing leverage
(d) Operating leverage/financing leverage - Calculate degree of financial leverage of XYZ Ltd.-
EBIT 12,000
Equity share capital 30,000
14% Preferance share capial 20,000
10% Debentures 50,000
Corporate tax rate 30%
(a) 0.4
(b) 4
(c) 1.4
(d) 4.44 - _________ involves increasing the proportion of debt and preference share in total capital.
(a) Trading on equity
(b) Capial Budgeting
(c) Financial decision
(d) financial analysis - Which of the following is not a type of financial lease arrangement?
(a) Leveraged lease
(b) Sale and lease back
(c) Indirect leasing
(d) Cross-border lease - A manufacturing company has an expected usage of 50,000 units of certain product during the next year. the cost of processing an order is Rs.20 and the carrying cost per unit is Rs.1 for two years EOQ is-
(a) 2,000 units
(b) 1,414 units
(c) 141 units
(d) 2,200 units - Which of the following matches is incorrect regarding approaches of valuation of HR?
(a) Historical cost approach – considers total cost of acquisition of human resource
(b) Replacement cost approach – considers the cost to replace a firm’s exiting HR
(c) Opportunity cost approach _ considers the value of alternative use of HR
(d) Economic value approach – considers the future value of the services that expected to render in present - Which of the following is a basic accounting equation?
(a) Assets = Capital + Liabilities
(b) Capital + Liabilities – Assets
(c) Assets – Liabilities – Capital
(d) All of the above - Which of these best explains fixed assets?
(a) It is for conversion into cash.
(b) It is an expensive item bought for the business.
(c) It is the item which will not wear out quickly.
(d) It is having long life specifically for resale. - Which of the following statement is NOT an objective of accounting?
(a) To provide information about the enterprise’s assets,liabilities and capital.
(b) To provide information on the personal assets and liabilities of the owner of an enterprise.
(c) To maintain records of business.
(d) To provide information on the performance of an enterprise. 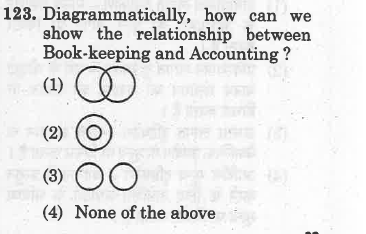
- The basic sequence in the accounting process can be best described as-
(a) Transaction,Journal,entry,source document,Ledger account,trial balance
(b) Transaction,source document,Journal entry,trial balance,Ledger
(c) Transaction,source document,Journal entry,Ledger account,trial balance
(d) source document,Journal entry,Transaction,Ledger account,trial balance - Which of following statement is true?
(a) Accrual concept implies accounting on cash basis.
(b) Patent right is in the nature of real account.
(c) Account involves only the recording of business transaction.
(d) Short term of accounting the user of accounting information. - Revenue is generally recognised being earned at the point of time when-
(a) Order is received.
(b) Production is completed.
(c) Goods are delivered.
(d) Cash is received. - Which of the following is not an external user of accounting information?
(a) Manager
(b) Creditor
(c) Potential investor
(d) Redearcher - According to going concern concept,business is viewed as having
(a) Long life
(b) An indefinite life
(c) Average life
(d) A limited life - According to which concept, in determining the net income from business, all costs which are applicable to revenue of the period should be charged against that revenue?
(a) Matching concept
(b) Cost concept
(c) Money measurement concept
(d) Dual aspect concept - Which of the following combination is/are not correct?
(A) Appending notes to the financial statements – full disclosure principal
(B) Valuation of stock at lower of cost or net realisable value – conservatism principal
(C) Making provision for doubtful debts – Materiality principal
(D) Following of WDV method for depreciating a particular asset year after year – consistency principal
(a) Only A,B
(b) Only C
(c) only C,D
(d) only B - Under Indian AS-2, Which of the following inventory items are not valued?
(a) Manufactured inventory items
(b) Biological inventory items
(c) Retail inventory items
(d) Industrial inventory items - Indian AS-10 represents –
(a) Events after the reporting period
(b) Accounting for fixed assets
(c) Property, Plant and equipment
(d) Related party disclosures - According to IFRS-10, the basis for consolidation is-
(a) Regulatory requirements
(b) Number of employees
(c) Size of share capital of the investee
(d) Control - IFRS-13 defines
(a) Consolidated financial statements
(b) Fair value measurement
(c) Operating segments
(d) Financial instrument - Ledger is bool of
(a) Original entry
(b) Secondary entry
(c) All cash transactions
(d) All non cash transactions - On purchase of a machine Rs.500 is paid to worker as wage for installing the machine. which of the action is correct?
(a) Wages a/c be debited.
(b) Installation charges a/c be debited.
(c) Machinery a/c debited.
(d) None of these. - ‘Received an order for goods from Mr.A’ give journal entry.
(a) Purchase a/c Dr. to cash a/c
(b) Mr. A’s a/c to cash a/c
(c) Purchase a/c to Mr.A’s a//c
(d) No entry will be passed. - Statement-I: If the business has any liability the proprietor’s capital must be more than the total assets.
Statement-II: Purchase made from Mr.X for cash should be credited to Mr.X
(a) Both statement are correct.
(b) Both statement are incorrect.
(c) Only statement I is correct.
(d) Only statement I is incorrect. - Closing entries are recorded in –
(a) Journal proper
(b) Ledger
(c) Cash Book
(d) Balance Sheet - The credit note issued is used to prepare-
(a) Sale book
(b) Purchase book
(c) Sale return book
(d) Purchase return book - Which of the following is not true regarding trial balance?
(a) it is a statement,not an account.
(b) Closing balances of ledger are shown in trial balance.
(c) Final accounts of business are prepared with the help of trial balance.
(d) it is a system adopted to judge the mathematical accuracy of balance sheet. - If total of both sides of trial balance is not matched, it shows
(a) A transaction is entirely omitted from record in the original books.
(b) There is a compensating error.
(c) A transaction is posted on the correct side but the wrong account.
(d) A transaction is wrong posted in ledger from subsidiary books. - Which of the following transaction results increase in asset as well as increase in liability?
(a) Credit purchase of machinery
(b) Issue of bonus share
(c) Payment to creditors
(d) Written off goodwill - Adjustment entry for salary outstanding is-
(a) Salary a/c Dr. to cash a/c
(b) Salary a/c Dr. to salary outstanding a/c
(c) salary outstanding a/c Dr. to cash a/c
(d) salary outstanding a/c Dr. to cash a/c - In cash book, bank charges of Rs.125 was not recorded. the correct cash book adjustment is-
(a) It will be credited in cash book.
(b) it will be credited in cash book.
(c) No adjustment needed in the cash book.
(d) Charges will be added to the cash book balance. - This is not the characteristic of bills of exchange
(a) It must be in writing
(b) It must be dated.
(c) It is an order to pay.
(d) It is a promise to pay. - P and Q are partners in a firm. State which claim is/are valid if the partnership agreement is silent in the following matters.
(A) P is an active partner. he wants a salary of Rs.10,000 per month.
(B) Q had advanced a loan to the firm. he claims interest @ 10% p.a.
(C) P has contributed Rs.20,000 and Q Rs.50,000 as capital. P wants equal share in profits.
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) Only C
(d) All A, B and C - Goodwill of a firm of A and B is valued at Rs. 12,000. it is appearing in the books at Rs. 7500 C is admitted he is supposed to bring for goodwill?
(a) Rs.12,000
(b) Rs.7,500
(c) Rs.2,000
(d) Rs.4,500 - What treatment is made of accumulate profits on the retirement of a partner?
(a) Credited to all partner’s capital accounts in old ratio.
(b) Debited to all partner’s capital accounts in old ratio.
(c) Credited to remaining partner’s capital accounts in new ratio.
(d) Credited to remaining partner’s capital accounts in gaining ratio. - On dissolution of the partnership firm, partner’s capital accounts are closed through
(a) Realisation through
(b) Bank account
(c) Drawing account
(d) Loan accountAnswer Key
1 (a) 2 (b) 3 (a) 4 (d) 5 (d) 6 (b) 7 (a) 8 (d) 9 (b) 10 (a) 11 (a) 12 (b) 13 (c) 14 (a) 15 (b) 16 (c) 17 (d) 18 (c) 19 (a) 20 (d) 21 (d) 22 (c) 23 (a) 24 (b) 25 (c) 26 (b) 27 (c) 28 (a) 29 (c) 30 (d) 31 (c) 32 (c) 33 (a) 34 (b) 35 (c) 36 (b) 37 (d) 38 (a) 39 (b) 40 (c) 41 (a) 42 (d) 43 (b) 44 (a) 45 (c) 46 (c) 47 (d) 48 (b) 49 (d) 50 (c) 51 (a) 52 (d) 53 (a) 54 (d) 55 (d) 56 (c) 57 (a) 58 (b) 59 (c) 60 (d) 61 (b) 62 (d) 63 (d) 64 (b) 65 (b) 66 (d) 67 (c) 68 (a) 69 (b) 70 (a) 71 (c) 72 (b) 73 (c) 74 (a) 75 (b) 76 (c) 77 (d) 78 (a) 79 (d) 80 (d) 81 (c) 82 (b) 83 (b) 84 (d) 85 (d) 86 (a) 87 (c) 88 (a) 89 (b) 90 (c) 91 (d) 92 (a) 93 (c) 94 (a) 95 (d) 96 (b) 97 (a) 98 (c) 99 (d) 100 (b)101 (a) 102 (c) 103 (b) 104 (c) 105 (a) 106 (b) 107 (c) 108 (b) 109 (c) 110 (c) 111 (d) 112 (c) 113 (a) 114 (a) 115 (b) 116 (a) 117 (c) 118 (a) 119 (d) 120 (a)121 (d) 122 (b) 123 (b) 124 (c) 125 (b) 126 (c) 127 (a) 128 (b) 129 (a) 130 (b) 131 (b) 132 (a) 133 (d) 134 (b) 135 (b) 136 (c) 137 (d) 138 (b) 139 (a) 140 (c) 141 (d)142 (d) 143 (a) 144 (b) 145 (a) 146 (d) 147 (c) 148 (c) 149 (a) 150 (b)
