- Gilt edged securities refer to
(a) Government securities
(b) Securities issued by municipal corporations
(c) Securities issued by first class companies
(d) None if these - C.R.A. is banking parlance stands for
(a) Credit rating association
(b) Credit rating agency
(c) Credit risk assessment
(d) None of these - Banking ombudsman means
(a) Person appointed to recover dues from defaulting borrowers
(b) A person to when customer can approach for redress of his grievances
(c) A person appointed to settle dispute between employees and management
(d) A person appointed by RBI to oversee the functioning of foreign banks - At what frequency can banks pay interest on saving bank account as per RBI guidelines?
(a) Monthly
(b) Quarterly
(c) Half Yrarly
(d) Yearly - Under which principal is the treasurer entitled to succeed to all rights of the insured regarding the subject matter of insurance after the claim of insurance has been fully and finally settled?
(a) Principal of indemnity
(b) Principal of subrogation
(c) Principal of insurance
(d) Principal of causapromima - Which one of the following securities cannot be issued by a public limited company in India?
(a) Participatory preference shares
(b) Redeemable preference shares
(c) Deferred shared
(d) Debentures - A country’s terms of trade are generally determined by
(a) The value of gold reserve held by its central bank
(b) Supply and demand in the world market
(c) Its rate of capital formation
(d) The number of competitors whose economics are based on the free market - Euro currency market is an international banking market whose major location is in
(a) London
(b) Germany
(c) France
(d) Norway - The main objective of micro finance systems
(a) Credit supply to poor
(b) Financial services inclusion to poor
(c) Involvement in business to poor
(d) Upliftment to poor - Venture capital is a long term commitment of investment in business and investment is based on
(a) Past truck record
(b) Regular return
(c) Credibility of the projects success
(d) None of all - The VSAT communication network for banks and financial institutions launched by RBI is known as
(a) SWIFT
(b) SBI NET
(c) BANK NET
(d) INFINET - The regulatory authority for the activities of merchant bankers in India is
(a) RBI
(b) Ministery of finance
(c) SEBI
(d) Indian bank association - The lowering of CRR is aimed at
(a) Increasing the supply of credit of commercial baks
(b) Increasing the value of rupee in the foreign exchange market
(c) Decreasing the lending capacity of the commercial bank
(d) Reducing the supply of money - Commercial paper are
(a) Undecured promissory notes
(b) Secured promissory notes
(c) Sold at the premium
(d) Issued for a period of 1 to 2 years - The essential condition of equilibrium under price discrimination is
(a) MRa – MRb =MC
(b) MRa – MRb < MC
(c) MRa – MRb >MC
(d) MRa>MRb >MC - Marginal revenue is _______at maximum total revenue and negative beyond that point
(a) +1
(b) -1
(c) Zero
(d) None 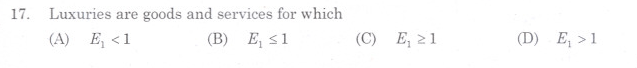
- The competition Act was enacted in the year
(a) 2002
(b) 1930
(c) 1986
(d) None of the above - Which one is not included in economic environment of external environment?
(a) Industry
(b) Transportation
(c) GNP
(d) Product life cycle - Chi-square and ‘t’ distribution are both
(a) Always symmetrical distribution
(b) Used for hypothesis testing
(c) Dependent on DOF
(d) Both b & c but not a - “Decision tree” in a business enterprises
(a) Improve organizational effectiveness
(b) Reduces the work load of employees
(c) Enhances workers participation in management
(d) None of the above - Which of the following is not one of the seven major parts to the research report?
(a) Results
(b) Abstract
(c) Method
(d) Footnotes - “Research methods”-
(a) Is a term used to refer to all aspects of the implementation of methods
(b) Are the procedures a researcher uses to gather information
(c) Are a set of abstract concepts together with propositions about they are related
(d) None of the above - Which of the following is a relative measure of dispersion?
(a) Standard deviation
(b) Variance
(c) Coefficient of variation
(d) All of the above - Which of the following is correctly matched?
(a) Pictogram – oral presentation of data
(b) Histogram – graphic presentation of data
(c) Histogram – diagrammatic presentation of data
(d) Cartogram – diagrammatic presentation of data - Which of the following will give a more “accurate” representation of the population from which a sample has been taken?
(a) A large sample based on the convenience sampling technique
(b) A small sample based on the simple simple random sampling
(c) A large sample based on simple random sampling
(d) A small cluster sample - The doctrine of indoor management implies that
(a) The outsiders need not necessarily known about the internal management of the company other than what is stated in articles of association
(b) The outsiders have the rights to think that the internal management as per the articles of association
(c) Both are right
(d) None of the above - Classical condition is a theory of
(a) Attitude
(b) Learning
(c) Perception
(d) Behaviour - Horizontal co-ordination is related to
(a) Co-operation
(b) Interested parties
(c) Differential level of management
(d) Equal level of management - Operating lease is favoured by the lessee in respect in respect of assets which depreciate in value on account of
(a) Obsolescence
(b) Wear and tear
(c) Exhaustion
(d) Passage of time - International financial management involves varied problems because
(a) It involves large number of transactions
(b) The business environment has to operate in different environments
(c) There is risk involved in dealing with unknown parties
(d) Financial management differs from one country to another country - The value of inventory will be the least in case of:
(a) Aggregate of total inventory method
(b) Item by them method
(c) Group method
(d) None of the above - Conversion cost is the sum total of
(a) Direct material & Direct labour cost
(b) Direct wages direct expenses and factory overheads
(c) Indirect wages and factory overheads
(d) Total of all direct expences - Observing changes in the financial variables across the years
(a) Vertical analysis
(b) Horizontal analysis
(c) Inter-firm analysis
(d) None of the above - Cash from operation is equal to
(a) Net profit plus increase in outstanding expenses
(b) Net profit plus increase in debtors
(c) Net profit plus increase in stocks
(d) Net profit plus increase in prepaid expenses - Overhead cost variance is the difference between
(a) Recovered overheads and actual overheads
(b) Budgeted overheads and actual overheads
(c) Budgeted overheads and standard overheads
(d) Budgeted overheads and recovered overheads - The costing method in which fixed factory overheads are added to inventory is
(a) Direct costing
(b) Marginal costing
(c) Absorption costing
(d) Standard costing - Internal rate of return is the rate of return
(a) That is associated with the internally generated fund
(b) The is used for internal calculations
(c) That discounts the future cash flow streams
(d) Rate of return earned on the initial investment in the project - In which of the following cases will a project not be accepted?
(a) Net present value>0
(b) 0< benefit cost ratio <1
(c) 0 < net benefit cost ratio <1 (d) All of the above - Float denotes the
(a) Difference between bank balance and the balance shown in the firm’s books
(b) A instrument to expedite cash inflows
(c) Difference between cash inflows and outflows
(d) None of the above - Which of the following models on dividend policy stresses on the investor’s preference for the current dividend?
(a) Traditional model
(b) Walter model
(c) Gordon model
(d) Miller and Modigliani model - If 182 days T-Bills are issued at a discount pride of Rs.96.52 then the yield is
(a) 6.98%
(b) 7.13%
(c) 7.23%
(d) 7.58% - Rent theory of profit is associated with the name of ?
(a) Hawley
(b) Walker
(c) Schumpeter
(d) J.B.Clark - Risk theory of profit was advocated by?
(a) Hawley
(b) JR.Clark
(c) Marshall
(d) Schumpter - ‘Sensitivity Training’ is a function of
(a) Planning
(b) Directing
(c) Leadership
(d) Staffing - ‘SWOT’ is used for
(a) Planning
(b) Organizing
(c) Motivating
(d) Controlling - Credit creation is possible
(a) To limited extent
(b) To any extent
(c) To the extent of the multiplier
(d) None of these - What is “Bank Rate” in India at present?
(a) 6%
(b) 7%
(c) 9.5%
(d) 8% - A line drawn from origin reflects
(a) Scale
(b) Proportion
(c) Both above
(d) None of the above - A risk free stock has a beta of
(a) -1
(b) Zero
(c) 0.5
(d) 1 - A security is said to be aggressive when n
(a) Has a beta of >1
(b) Plots on the upper pary of SML
(c) Gives below average returns
(d) Both a and b above - Which of the following is not a non diversifiable risk?
(a) Interest rate risk
(b) Purchasing power risk
(c) Operating risk
(d) Market risk - Which is an example of pegged currency?
(a) Sterling
(b) Malaysian Ringgit
(c) Australian Dollar
(d) Argentine peso - Which of the following methods does a firm resort to avoid dividend payments?
(a) Share splitting
(b) Declaring bonus shares
(c) All of the above
(d) Both a and b - Buying and selling call or put option with the same strike price but different expiration dates is called
(a) Long hedge
(b) Short hedge
(c) Horizontal option spread
(d) Nearby contract - Why do you need to review the existing literature?
(a) To make sure you have a long list of references
(b) Because without it,you could never reach the required word-count
(c) To find out what is already known about your area of interest
(d) To help in your general studying - Sampling frame is-
(a) A summary of the various stages involved in designing a survey
(b) An outline view of all the main clusters of unit in a sample
(c) A list of all the units in the population from which a sample will be selected
(d) A wooden frame used to display tables of random numbers - What is difference between a bar chart and histogram?
(a) A histogram does not show the entire range of score in a distribution
(b) Bar charts are circular,whereas histogram are square
(c) There are no gaps between the bars on a histogram
(d) Bar charts represents numbers,whereas histogram represent percentages - What is meant by a ‘spurious’ relationship between two variables?
(a) One that is so ridiculously illogical it cannot possibly be true
(b) An apparent relationship that is so curious it demands further attention
(c) A relationship that appears to be true because each variable is related to a third one
(d) One that produces a perfect negative correlation on a scatter diagram - The sampling distribution refers to:
(a) The distribution of the various sample sizes which might be used in a given study
(b) The distribution of the different possible values of the sample mean together with their respective probabilities of occurrnce
(c) The distribution of the values of the items in the population
(d) The distribution of the values of the items actually selected in a given sample - The normal distribution is a
(a) Discrete distribution
(b) Continuous distribution
(c) Positively skewed distribution
(d) None of the above - Soundness of a tool is adjudged by
(a) Testing validity
(b) Testing reliability
(c) Pilot testing
(d) Both a & b 
- “Sensitivity training” is a function of
(a) Planning
(b) Directing
(c) Leadership
(d) Staffing - The lack of faith and confidence of managers in subordinate is an important barrier of
(a) Effective leadership
(b) Effective control
(c) Effective delegation
(d) Effective direction - Management by objectives (MBO) is not only a technique of management but is philosophy of management “was said by”
(a) F.W. Taylor
(b) Chester Bernard
(c) Peter Drucker
(d) Henry Fayol - The important principal propounded by Graicunas is
(a) Principals of Span of Control
(b) Principals of Balance
(c) Principals of standardization
(d) Principals of delegation - An enterprise get more output and mutual co-operation from its subordinates by adopting?
(a) Motivation by leadership
(b) Motivation by participation
(c) Motivation by goals
(d) Motivation by change - Herzberg’s theory of motivation is known by the name
(a) Need hierarchy theory
(b) Theory X
(c) Hygiene theory
(d) None of the above - Extreme of decentralization is called as
(a) Bottom up management
(b) Autonomy
(c) Departmentalization
(d) Leadership management - The effective principal of direction does not include
(a) Harmony of objective
(b) Effective leadership
(c) Effective communication
(d) Personality - The certificate to commerce business is to be called for perusal and returned for opening of an account of
(a) Public limited company
(b) Club and association
(c) Private limited company
(d) Trust - Which is the smallest organizational sub unit for which separate cost allocation is attempted?
(a) Cost unit
(b) Cost centre
(c) Costing
(d) Management costing - The process of managing the sales ledger of a client by a financial service company is called
(a) Forfeiting
(b) Factoring
(c) Leasing
(d) Securitization of debt 
- The instruments that are “marked” to market are
(a) Forwards
(b) Futures
(c) Swaps
(d) Options - In an options contract that can be exercised only at the time of maturity is called
(a) Double option
(b) American option
(c) Put option
(d) European option - Red ink interested is noted in which one of the following?
(a) Current account
(b) Account current
(c) Capital account
(d) Cash account - Valuation balance sheet is prepared by
(a) LIC
(b) GIC
(c) Govt.companies
(d) Public utility companies - When key factor is operating the formula for calculating profitability is
(a) Contribution/key factor
(b) Sales/key factor
(c) Profit/key factor
(d) None of the above - Depreciation is charged against
(a) Profit
(b) Assets
(c) Company
(d) Books of account - Sales value variance is the difference between
(a) Standard sales and actual sales
(b) Budgeted sales and actual sales
(c) Budgeted sales and standard sales
(d) None of the above - Privatization of ownership through sale of equity share is called
(a) Denationalization
(b) Disinvestment
(c) Contracting
(d) None of the above - Bills receivable is dishonored implies
(a) No change in current ratio
(b) Current ratio declined
(c) Current ratio is improved
(d) None of these - Writing off the expired cost of intangible assets is called
(a) Amortization
(b) Capitalization
(c) Depletion
(d) Depreciation - To measure change in total monetary worth one should calculate
(a) Private index
(b) Quantity index
(c) Value index
(d) None of the above - Sensex is based on
(a) 50 shares
(b) 30 shares
(c) 60 shares
(d) 40 shares - Prospect theory is related to
(a) Marketing
(b) Finance
(c) HR
(d) Psychology - SEC means
(a) Security and exchange commission
(b) Stock exchange commission
(c) Special exchange commission
(d) Script exchange commission - The dividend paid on the preference share is not deductible expenditure for_____.
(a) Corporate tax
(b) Gift tax
(c) Income tax
(d) Property tax - The term Allonge refers to
(a) The sheets of paper used in writing a dead
(b) The stamps affixed on document
(c) A sheet of paper attached to mortagage deed for the purpose of witness
(d) A share of papers attached to a negotiable instrument for the purpose of making endorsement thereof when there is no space in the instrument - Which of the following factor increase the growth rate of the compnay?
(a) External borrowing
(b) Increase of corporation’s relation rate
(c) Increase the corporation’s rate of return
(d) All of the above - Opportunity cost helps in
(a) External borrowings
(b) Increase of corporation’s retention rate
(c) Increase the corporation’s rate of return
(d) All of the above - A growth company is one where
(a) r = Ke
(b) rKe
(d) None - The ability of a firm in employing loan funds having a fixed interest to engance returns to the owner is known as
(a) Leverage
(b) Trading on equity
(c) Income gearing
(d) None of all - In a bullish market it is better to buy shares whose beta is
(a) More than 1
(b) Less than 1
(c) Equal to 1
(d) Negative - Purchase and sale of shares before or after official trading hours of stock exchange is known as
(a) Margin trading
(b) Short selling or short buying
(c) Kerb trading
(d) Hannering - A low proprietary ratio reflects
(a) Sound capital structure of the company
(b) Over-trading
(c) Proprietors have larger stab in company
(d) None of the above - Which of the speculator expect price of the securities to rise in near future?
(a) Stag
(b) Bull
(c) Bear
(d) None of the above - Under tax credit method VAT is equal to
(a) Sum of wages profits rent and interest
(b) Out put – Input
(c) Percentage of sales
(d) Tax charged on sales – Tax paid on inputs
